Apple is overhauling the cryptographic safety of iMessage by introducing a brand new messaging protocol to thwart superior computing that has but to develop into a possible risk, and doubtless will not for years.
Apple already contains end-to-end encryption in its safe iMessage platform. However whereas components akin to Contact Key Verification may also help preserve customers safe from current-generation computing threats, it might have a tough time taking up quantum computing.
To thwart quantum computer systems after they finally develop into extra generally used, Apple will not be ready till they arrive to bolster its safety.
As described in an Apple Safety Analysis Weblog submit on Wednesday, Apple needs to guard communications which might be occurring now from the long run risk by introducing a brand new cryptographic protocol to iMessage known as PQ3.
Harvest Now, Decrypt Later
Encryption depends on mathematical issues and algorithms to keep up safety, with extra advanced fashions providing extra safety just by the character of how encryption is damaged. If a foul actor can’t get the important thing to interrupt the encryption, they as a substitute must depend on brute-forcing each potential mixture of keys to defeat the algorithm.
For present computer systems, it is a time and resource-intensive process to crunch by each single risk till the suitable one is found. Nonetheless, quantum computer systems have the potential to do the identical calculations shortly, breaking encryption.
Nonetheless, quantum computing remains to be not obtainable since it’s nonetheless being labored on, and is not commercially viable to roll out to a wider viewers For the second, quantum computing is not a problem, however sooner or later sooner or later, it might be.
Banking on the likelihood that quantum computing will develop into extra widespread sooner or later, unhealthy actors are nonetheless holding onto encrypted knowledge they cannot entry now, within the perception they’ll decrypt the info down the highway. It’s an assault state of affairs known as Harvest Now, Decrypt Later, and one which depends extra on low cost storage than the expense of attempting to interrupt safety by brute drive.
Harvest Now, Decrypt Later does theoretically imply that every one presently encrypted communications is in danger from future publicity by somebody wholesale gathering communications, on the expectation that will probably be simpler to do with quantum computing.
Publish-quantum cryptography
To attempt to decrease the dangers from using quantum computing, cryptographers have labored on post-quantum cryptography (PQC). This consists of latest public key algorithms which might be turning into the idea of quantum-secure protocols, particularly protocols that can be utilized by present non-quantum computer systems, however which might be nonetheless safe when put towards quantum computer systems.
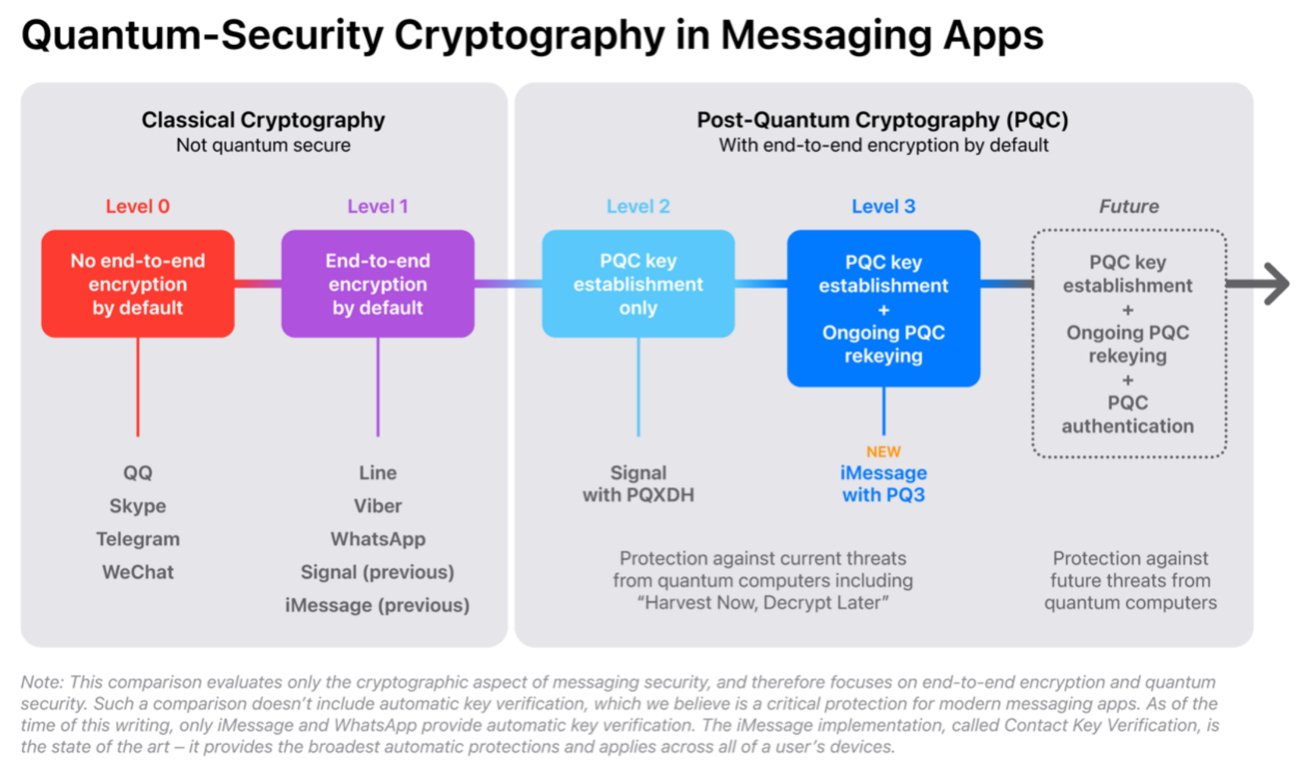
Apple describes the state of quantum cryptography in messaging purposes in a tiered method, growing with the extent quantity. Degree 0 and Degree 1 are deemed Classical Cryptography with out quantum safety, whereas Degree 2 and later are categorized as utilizing PQC.
Degree 0 is for messaging methods with none use of quantum safety, nor do they use end-to-end encryption by default. This contains Skype, QQ, Telegram, and WeChat.
Degree 1 remains to be not classed as quantum-secure, but it surely does embrace end-to-end encryption by default. Providers utilizing this embrace Line, Viber, WhatsApp, and the earlier model of iMessage.
Shifting to PQC ranges, Sign is the primary and solely large-scale messaging app to be classed as Degree 2, with its assist for the Publish-Quantum Prolonged Diffie-Hellman (PQXDH) key settlement protocol. This principally makes use of public keys for 2 events to mutually authenticate one another firstly of a dialog.
Nonetheless, even Degree 2 has its points, in line with Apple, because it solely supplies quantum safety if the dialog key is not compromised. An attacker can probably have the means to compromise encryption keys, offering entry to the encrypted conversations till the keys are modified.
By commonly altering the keys, this locations a restrict on how a lot of a dialog an attacker might see if a key’s compromised. That is the case each for acquired key entry and for quantum processing makes an attempt.
With this line of pondering, Apple says that apps ought to attempt to obtain Degree 3 safety, when PQC is utilized in securing the preliminary institution of keys for communications in addition to the continued message trade. Degree 3 must also embrace the flexibility to robotically restore cryptographic safety, even when a key’s compromised.
iMessage and PQ3
Apple’s announcement is that it has give you a brand new cryptographic protocol it calls PQ3 that can be included into iMessage. The change presents “the strongest safety towards quantum assaults,” with iMessage turning into the primary and solely to assist Degree 3 safety.
The rollout of PQ3 to iMessage will begin with the general public releases of iOS 17.4, iPadOS 17.4, macOS 14.4, and watchOS 10.4, and has already been included into developer previews and beta releases. Present iMessage conversations between gadgets that may assist PQ3 can be robotically altering over to the brand new protocol.
Apple provides that, because it “positive factors operational expertise with PQ3 on the large international scale of iMessage,” PQ3 will substitute current cryptographic protocols inside all supported conversations by the tip of 2024.
There have been quite a lot of necessities wanted by Apple for PQ3 to work correctly. This included introducing post-quantum cryptography from the beginning of a dialog, in addition to limiting how a lot of a dialog might be decrypted with a single compromised key.
It additionally had to make use of a hybrid design that mixes post-quantum algorithms with present Elliptic Curve algorithms in order that PQ3 can’t be much less protected than current-gen protocols. There’s additionally a must amortize the message measurement, lowering the overhead of further safety.
Lastly, it wants to make use of formal verification strategies that may “present sturdy safety assurances for the brand new protocol,” Apple writes.
On this final level, Apple has already gone to nice lengths to formally confirm PQ3’s effectiveness, together with an in depth evaluation from multi-disciplinary groups in Apple’s Safety Engineering and Structure, in addition to foremost consultants in cryptography.
A group led by Professor David Basin, the pinnacle of the Info Safety Group at ETH Zurich, in addition to Professor Douglas Stebila of the College of Waterloo, have researched post-quantum safety for web protocols. Every used completely different mathematical approaches to display PQ3 will stay safe as long as the underlying cryptographic algorithms maintain up.
Apple additionally introduced in a number one third-party safety consultancy to independently assess PQ3’s supply code, and located no safety points.
How PQ3 works
PQ3 makes use of a brand new post-quantum encryption key within the public keys the gadgets generate regionally, that are despatched to Apple’s servers for iMessage registration. This course of lets sender gadgets get the receiver’s public keys and to generate post-quantum encryption keys from the very first message and preliminary key institution, even when the recipient is offline.
A “periodic post-quantum rekeying mechanism” can also be included inside conversations, which might self-heal the safety from key compromises. New keys despatched with conversations are used to create recent encryption keys, which can’t be computed by evaluation of earlier keys, additional sustaining safety.
Attackers would additionally must beat the hybrid design that mixes each the Elliptic Curve and post-quantum components for preliminary key institution and for rekeying.
The rekeying course of includes the transmission of latest public key materials in-band with encrypted gadgets that gadgets are exchanging with one another. New public keys primarily based on Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman (ECDH) are transmitted consistent with responses.
Because the post-quantum key’s a lot bigger than present current protocols, Apple minimizes the affect of the dimensions by making the rekeying course of occur periodically, as a substitute of each message.
The situation of whether or not to rekey and transmit is one which tries to stability the dimensions of messages in a dialog, the expertise of customers with restricted connectivity, and the necessity to keep infrastructure efficiency. Apple provides that, if it is wanted sooner or later, software program updates might improve the rekeying frequency, whereas preserving the system backward-compatible with all PQ3-supporting {hardware}.
After implementing PQ3, iMessage will proceed to make use of basic cryptographic algorithms to authenticate senders and confirm the Contact Key Verification account key, because it says the mechanisms usually are not in a position to be attacked retroactively by future quantum computer systems.
To insert itself into the center of an iMessage dialog, an attacker would want a quantum pc that might break an authentication key earlier than or on the time the communication takes place. Apple claims this thwarts Harvest Now, Decrypt Later situations because it requires a quantum pc able to performing the assault on the time of the communication itself.
Apple believes the potential to assault the brand new protocol is “a few years away,” however its safety group insists it’s going to proceed to evaluate the wants of post-quantum authentication to defeat future assaults.