The risk actors related to the 8220 Gang have been noticed exploiting a high-severity flaw in Oracle WebLogic Server to propagate their malware.
The safety shortcoming is CVE-2020-14883 (CVSS rating: 7.2), a distant code execution bug that could possibly be exploited by authenticated attackers to take over inclined servers.
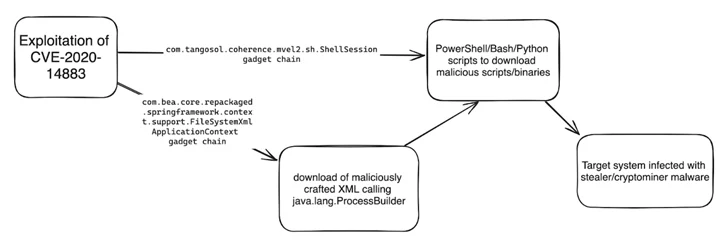
“This vulnerability permits distant authenticated attackers to execute code utilizing a gadget chain and is often chained with CVE-2020-14882 (an authentication bypass vulnerability additionally affecting Oracle Weblogic Server) or using leaked, stolen, or weak credentials,” Imperva stated in a report printed final week.
The 8220 Gang has a historical past of leveraging recognized safety flaws to distribute cryptojacking malware. Earlier this Could, the group was noticed using one other shortcoming in Oracle WebLogic servers (CVE-2017-3506, CVSS rating: 7.4) to rope the units right into a crypto mining botnet.
Current assault chains documented by Imperva entail the exploitation of CVE-2020-14883 to specifically craft XML recordsdata and finally run code liable for deploying stealer and coin mining malware equivalent to Agent Tesla, rhajk, and nasqa.
“The group seems to be opportunistic when deciding on their targets, with no clear development in nation or trade,” Imperva safety researcher Daniel Johnston stated.
Targets of the marketing campaign embody healthcare, telecommunications, and monetary companies sectors within the U.S., South Africa, Spain, Columbia, and Mexico.
“The group depends on easy, publicly obtainable exploits to focus on well-known vulnerabilities and exploit simple targets to attain their targets,” Johnston added. “Whereas thought-about unsophisticated, they’re consistently evolving their techniques and strategies to evade detection.”