The SEI conducts unbiased technical assessments (ITAs) periodically for any packages that request them, each technical and programmatic features. Such requests typically come from both packages which might be experiencing challenges with delivering their techniques or from exterior stakeholders to verify on the progress that’s being made. In the midst of performing such an evaluation, the ITA crew could interview as many as 50 to 100 folks from the program administration workplace (PMO) workers, contractor workers, customers, and different exterior stakeholder organizations, all below assurance of anonymity. Interviewees usually give very open and candid responses, giving the crew perception into what is definitely occurring on a program and the flexibility to achieve a deep understanding of the pressures and incentives below which individuals are working.
One notable facet of such assessments is that related issues come up throughout separate and dissimilar packages. The important thing questions that come up when conducting assessments of many alternative packages are “Why do a few of these hostile behaviors maintain occurring throughout completely totally different packages?” and “Is there a strategy to cease them?” On this weblog publish, I talk about the recurring downside in software program acquisition and improvement of what I name clinging to the outdated methods. I describe the habits within the context of a real-world situation and supply suggestions on recovering from and stopping future occurrences of this downside. Future posts on this collection will discover different recurring issues.
About Acquisition Archetypes
The SEI’s work on all these recurring patterns of habits relies on our experiences doing assessments of enormous authorities packages, and employs ideas from techniques considering to research dynamics which have been noticed in software program improvement and acquisition observe.
The Acquisition Archetypes, as we name them, are based mostly partly on the concept of the extra basic techniques archetypes. Acquisition Archetypes describe recurring patterns of failure noticed in acquisition packages with the intent of creating folks conscious of them and their results and supply folks with approaches to mitigate or keep away from them. (See among the earlier SEI work in Acquisition Archetypes.)
Within the majority of circumstances, the incentives at work in acquisition packages don’t change a lot from program to program, and so are inclined to drive related behaviors throughout a variety of acquisition packages. Taken collectively, these incentives are analogous to the legal guidelines of physics for nature in that they drive the behaviors of all organizations.
The archetype I current on this publish is said to the introduction of a brand new expertise and technique. I illustrate it within the context of utilizing DevSecOps as a result of it’s a newer portfolio of applied sciences that’s being utilized to key DoD acquisition packages. Nevertheless, this archetype would apply equally effectively to many different new, disruptive applied sciences—underscoring the purpose that regardless of the various adjustments in expertise and the substantial variations throughout packages, the concepts underlying this archetype nonetheless apply.
Clinging to the Outdated Methods
Description
There’s a totally different pressure occurring inside acquisition packages that attempt to undertake new applied sciences and strategies: the technologists and engineers are thrown into battle with practical organizations which might be unfamiliar with and unaccustomed to doing enterprise in another way to assist the brand new expertise or technique. These practical organizations typically resist the adjustments that will enhance velocity and safety. There could also be some authentic causes for this resistance. For instance, the present interpretation of the rules below which they function could prohibit sure choices or actions.
A tradition of doing issues the same old or conventional method as a substitute of embracing newer approaches and applied sciences can create schisms throughout the program. These schisms are usually not stunning because it’s a significant tradition change to considerably evolve the strategies and insurance policies of any group. Modifications are being pushed by a lot of totally different new strategies and applied sciences—not simply DevSecOps, but additionally model-based techniques engineering (MBSE), digital engineering, synthetic intelligence/machine studying, and others. I concentrate on DevSecOps on this publish as a result of it has demonstrated unprecedented enhancements in DoD fielding occasions and safety, but additionally introduces extra engineering complexity and requires extra coordination and ability.
Some engineers could count on everybody to leap onboard with the brand new expertise and are shocked after they don’t and received’t. Some might imagine the functionals (the finance, authorized, safety, and contracting consultants) are old-fashioned and caught of their methods, or among the functionals might imagine the brand new expertise or technique is a passing fad that has little to do with the way in which they carry out their position. These opposing factors of view characterize a cultural battle that stems from the expertise. The extra the engineers attempt to pressure change on the functionals, the tougher these elements of the group are prone to push again in opposition to these adjustments.
An essential facet of this battle is that there are two chains of command for functionals: one which goes to this system they’re working for, and one which goes again to the bigger group they’re part of (e.g., finance, acquisition, and many others.). The extra revolutionary the technological change, the better the impression on the functionals who should assist its enterprise features. For instance, within the context of cybersecurity, as a substitute of the safety functionals adapting the safety strategy to the brand new applied sciences, the technologists are sometimes pressured to make use of the older applied sciences that the safety individuals are extra accustomed to. This aversion to newer applied sciences additionally has to do with the standard approaches of many years in the past versus the approaches being utilized by engineers at this time. The strain manifests in varied methods, resembling within the shift from waterfall to Agile/DevSecOps, or from conventional safety approaches to extra streamlined automated strategies, from monolithic certification on the finish of improvement to steady certification, and so forth.
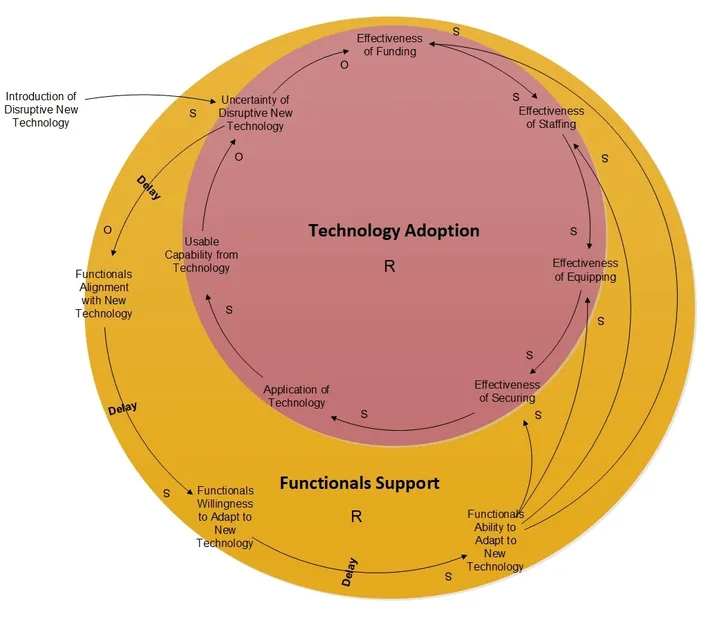
This battle is in the end resolved in one among two methods: Both a point of change is ultimately effected to get functionals’ buy-in and assist for adapting the present processes to the brand new expertise, or the expertise adoption is deemed unsuccessful and could also be discarded (Determine 1).
Reviews from the Area
One program that was adopting DevSecOps bumped into a wide range of points in supporting that strategy with the practical assist of acquisition, personnel, buying, and finance. As one official put it, “A part of the frustration on the acquisition aspect is the shortage of DevSecOps understanding.”
Equally, one other workers member stated, “Some folks don’t have any expertise with DevSecOps earlier than, so that they battle. The way in which they strategy packages, they’re functionally aligned, and matrixed to them, so there’s a battle generally to translate their work of finance and contracts to the technical folks.”
One other went as far as to say, “The predominant threat within the DoD house is individuals who don’t perceive DevSecOps and DevSecOps contracting, saying that this fashion of constructing software program is illegal—and I’ve been on calls with three authorities attorneys about that, the place they have been arguing that it was unlawful to construct software program that method. There’s a DoD publication for constructing software program, and the way DoD buys software program. It’s all about waterfall—however nobody builds software program like that anymore. New memos have come out that make DevSecOps buying approaches lawful now, however there’s nonetheless numerous concern on the market, and it’s onerous to persuade folks that it’s OK.”
One officer identified that, “We’ve got Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) insurance policies that haven’t modified in years, and acquisition has native insurance policies as effectively, and other people develop into annoyed.” One other stated “In acquisition it’s so troublesome to make one thing occur, you develop into pleased with something you will get. They go away contractual stuff in place for a number of years with out evolving it—however we’d by no means do this on the technical aspect. Individuals are afraid to ask to do one thing in another way.”
Whereas the speed of technical change appears to be growing, one workers member stated that most of the functionals are “…nonetheless residing in a world the place individuals are extra comfy with the outdated method of doing issues, and never as comfy with doing issues in a brand new method with new expertise. So, it’s the shortage of willingness to make use of digital expertise that issues me.” As one other acquisition official summed it up, “Nobody is how acquisition should change to assist DevSecOps”—and so there’s a massive and rising hole between the technical workers and the functionals who assist them.
With safety, “It comes off as a Nineteen Eighties safety strategy. As an alternative of adapting the safety to the brand new applied sciences, they pressure you to make use of the older applied sciences that they’re accustomed to as a substitute.” One other admitted that whereas “We would like implementations to be strong by way of safety, we’ve tried to implement safety that folks both don’t perceive, don’t care about, or each. Most PMs (program managers), most SPDs (system program administrators) don’t perceive, and neither do the SCAs (safety management assessors) or AOs (authorizing officers).”
By way of finance, there are some apparent points in supporting DevSecOps. As one practical famous, “We settle for cash from different packages, 3400 (O&M) and 3600 (RDT&E). We couldn’t combine colours of cash, however you nearly have to with DevSecOps.”
Concerning contracting for professional DevSecOps workers, a contracting official stated “[The contractor] drives us loopy. They’re the costliest, they suppose they’re unicorns, and they also’re troublesome to barter. They comprehend it, and so they are available excessive on their charges. As a PCO (procuring contracting officer), I have to decide if the value is honest and cheap—and you need to justify that. Technical means is at all times extra essential than worth. Technical folks don’t perceive having to justify using a specific vendor.”
Regardless of the clear have to do issues in another way, one acquisition skilled said that “There are few acquisition people who find themselves true advocates of or champions for change. That progress piece is lacking.” The bigger downside is that “Everybody simply accepts the way in which issues are. How will you change your processes in an effort to do it higher and sooner? We are able to’t be content material with what we’ve got. We’ve got to be considering, what’s subsequent, and what can we make higher?”
In attempting to reply that query, one officer admitted that “The [functional] profession area is extra about checking packing containers to get promoted. It would take an overhaul in expertise administration and career-field administration to try this higher. You may as well assist to retrain some communities, however most likely not all.” For one officer, a key place to begin was acknowledging that “We should give you a method to assist DevSecOps. Individuals want a baseline understanding of DevSecOps.” Going additional, one other officer acknowledged that an Agile-based and DevSecOps-like strategy could possibly be utilized to the work of functionals as effectively, saying “We needs to be utilizing DevSecOps for functionals in the identical method that we’re already utilizing it for engineers/builders, by doing extra in the way in which of automation of repetitive duties, and establishing a special tradition that’s extra modern in utilizing the mechanisms that exist already. We could possibly be doing for acquisition what DevSecOps is doing for software program improvement.”
Options and Mitigations
Because of the dual-reporting construction of functionals within the army, some adjustments required to allow full assist of a brand new expertise, resembling DevSecOps, should happen effectively above the extent of this system workplace trying to undertake it.
A part of the issue is that every service has barely totally different takes on how they interpret the FAR and Protection Federal Acquisition Regulation (DFAR) guidelines—and people guidelines are longstanding and rigorously enforced, regardless that they’re solely interpretations of the unique rules. Revisiting the unique rules typically exhibits that they aren’t as restrictive as the following coverage interpretations have been—however years later these interpretations are nonetheless being rigidly utilized even after they now not serve both the present altering setting or the unique regulation they have been meant to implement.
One instance is the necessity to do right budgeting 5 years upfront of each deliberate piece of labor divided throughout analysis, improvement, check & analysis (RDT&E) versus operations and upkeep (O&M) expenditures, which characteristic nearly paralyzing guidelines relating to which kind of funding must be used for issues resembling direct replacements versus substitute upgrades. One other instance is the buying of software program licenses, the place there’s uncertainty relating to the allowed use of RDT&E versus O&M colours of cash within the first versus subsequent years of use. The cumulative impact is to constrain packages attempting to maneuver to extra versatile improvement fashions, resembling Agile and DevSecOps, and put their success in danger.
As alluded to earlier, contracting for professional DevSecOps workers may be troublesome. Likewise, staffing additionally performs a task within the profitable, or unsuccessful, adoption of DevSecOps. There are comparatively few DevSecOps engineers obtainable within the DoD, and DoD is straight competing with business by way of salaries and work setting when hiring that sort of expert expertise. Applications have difficulties staffing authorities billets with DevSecOps experience, missing applicable job classes and well-defined profession paths with adequate compensation, and forcing packages to backfill with contract workers—which presents its personal challenges. When army and civilian workers are in a position to be employed and skilled to work in DevSecOps roles, retention turns into a problem as business corporations work to poach them from their authorities roles into what are sometimes extra profitable business positions. The federal government even acts in opposition to its personal pursuits by rotating extremely expert army personnel out of DevSecOps positions to extra conventional (and sometimes much less attention-grabbing) acquisition billets requiring extra routine expertise the place their hard-won DevSecOps experience will not be relevant, and quickly declines.
To handle the coverage restrictions imposed on acquisition, finance, and contracting functionals, these workers must be skilled in using key new applied sciences resembling DevSecOps even when they’re indirectly utilizing them, in order that they’re conscious of the problems, perceive them and the objectives, and are thus higher outfitted to advertise and allow using the expertise. Technical workers also needs to develop into extra conscious of the totally different features of acquisition. A few of this coaching content material ought to come from accumulating collectively the insights from the experiences of personnel in software program factories about greatest use and leverage present insurance policies. A coaching curriculum alongside the traces of a DevSecOps for Managers needs to be the outcome, specializing in
- software program lifecycle processes, acquisition methods, and the total vary of various kinds of contracting automobiles
- how present mechanisms and contractual automobiles may be utilized in modern methods to assist DevSecOps
- making present coaching on DevSecOps extra related
- addressing the cultural and course of implications of DevSecOps adoption pertaining to acquisition
- involving DevSecOps consultants in modern coaching roles to show and construct new coursework
One other helpful strategy can be to institute an change program amongst acquisition, finance, and different practical workers working in numerous software program factories, in order that they might share and find out about totally different approaches which have been developed and utilized by different workers to handle related points and conditions.
As a extra strategic repair, DoD ought to proceed to check extra of the coverage adjustments that could be wanted on precise packages, based mostly on the varieties of key points they face. An instance of such a coverage experiment already occurring is the Finances Appropriation 8 (BA-8) software program funding single appropriation pilots, through which a single new appropriation class (coloration of cash) is created that can be utilized for each RDT&E and O&M appropriations. Such an appropriation would imply that packages wouldn’t need to finances particular quantities of RDT&E and O&M funding years upfront, probably proscribing their means to spend funding as wanted in a DevSecOps improvement, the place the event and upkeep actions are tightly intertwined and troublesome to separate.
To handle the problems of DevSecOps staffing over the long run, as this system workforce initially grows after which begins to show over, this system should interact in a big workforce enchancment and coaching or retraining exercise, and evolve towards a tradition that may retain such a complicated workforce:
- Mentor army officers in DevSecOps organizations with profitable business DevSecOps leaders to be taught new management kinds for high-tech groups.
- Survey the federal government and contractor workers usually (and report back to management) on their morale and the diploma to which the specified DevSecOps tradition is being achieved, and take further steps to advertise the tradition if the metrics are usually not transferring within the route and on the velocity required.
- Actively interact with native and regional universities to create a pipeline of future software program engineers with the DevSecOps expertise to assist the wants of this system throughout its lifespan.
- Institute externship packages or rotations between authorities and protection or business business companions to usually advance the ability units of key software program improvement workers.
- Advocate for brand spanking new compensation charges which might be extra applicable for hiring and retaining extremely expert DevSecOps positions (related to what’s performed for physicians, surgeons, pilot flight pay, and many others.).
- Advocate for devoted DevSecOps officer and civilian profession tracks past the standard software program profession fields.
- Calm down or receive waivers for army rotations for expert DevSecOps officers and enlisted personnel to enhance continuity in groups.
Lastly, a extra controversial strategy is perhaps to align further monetary or efficiency incentives to functionals who efficiently area their packages inside time/finances/high quality objectives, incentivizing general program efficiency in addition to coverage compliance.
The Outlook for DevSecOps Adoption
On this publish, I’ve regarded into one recurring program habits associated to the introduction of DevSecOps into the context of acquisition packages: a battle between builders and their supporting practical areas that aren’t accustomed to supporting this new method of growing software program.
Whereas it has many substantial advantages, DevSecOps has been—and for the foreseeable future will proceed to be—a robust however disruptive expertise with cooperation issues which might be pervasive all through acquisition. A few of these issues can’t be handled on the particular person program stage and will require some vital coverage adjustments throughout the DoD enterprise. The significance of DevSecOps to DoD software program improvement signifies that making the adjustments to coverage to have the ability to totally assist it should be a precedence.
In my subsequent weblog publish on this collection, I’ll talk about intimately one other recurring archetypal downside associated to DevSecOps adoption: vendor lock-in and the excessive value of switching distributors.